Reaktor Fusi
Vacuum Vessel
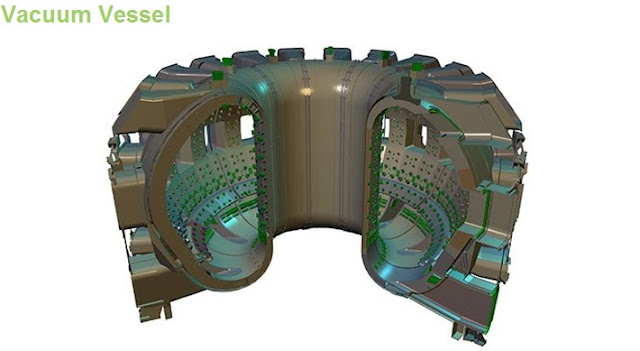
A cut-away of the ITER Vacuum Vessel showing the Blanket modules attached to its inner wall and the Divertor at the bottom.
The size of the Vacuum Vessel dictates the volume of the fusion plasma; the larger the vessel, the greater the amount of power that can be produced. The ITER Vacuum Vessel will be twice as large and sixteen times as heavy as any previous tokamak, with an internal diametre of 6 metres. It will measure a little over 19 metres across by 11 metres high, and weigh in excess of 5000 tons.
The ITER Vacuum Vessel with its 44 ports. At 8000 tons, the stainless steel vacuum vessel weighs slightly more than the Eiffel Tower.
The Vacuum Vessel will
have double steel walls, with passages for Cooling Water to circulate between them. The inner surfaces of the Vessel will be covered with Blanket Modules that will provide shielding from the high-energy neutrons produced by the fusion reactions. Some of the Blanket Modules will also be used at later stages to test materials for Tritium Breeding concepts.
Forty-four ports will provide access to the Vacuum Vessel for Remote Handling operations, Diagnostic systems, Heating, and Vacuum systems: 18 upper ports, 17 equatorial ports, and 9 lower ports.
Sumber:
Web Resmi ITER